
Molds are the most typical form of fungus found on earth, comprising approximately 25% of the earth’s biomass.
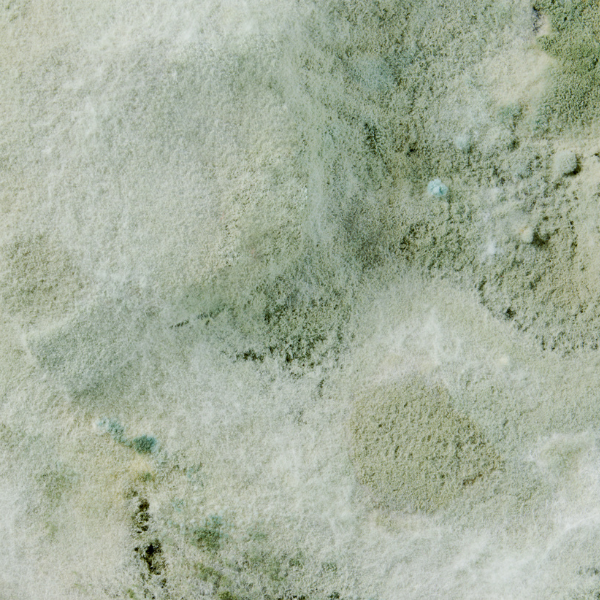
Molds are made up of masses of thread-like cells called hyphae. Under the appropriate conditions, the hyphae will grow into long intertwining strings that form the main body of the fungus, or the mycelium. It is the mass of mycelium that is visible to the human eye.
Molds reproduce via seed-like spores present in the air and soil. However, molds can also spread if a fragment of broken hyphae is transplanted to an area with adequate moisture and organic matter for food. Spores are produced in large numbers. They are located on the hyphae.
A mass of hyphae, called a mycelium, is frequently visible on the surfaces of bread and wood. A mycelium often takes the shape of a fan or a fluffy mat. Mycelium is the intertwined mass of hyphae that forms the mold colony. The mycelium is also known as the “body” or thallus of the mold.
Vegetative mycelium is composed of those hyphae that adhere to the substrate and absorbs nutrients. Aerial mycelium is composed of those hyphae that grow up from the surface and support the spores.
In some molds, the lower hyphae will form small root-like structures called rhizoids. Rhizoids act like branched roots that help anchor the hyphae to the substrate or food source. Most of the mold body is buried in the food material (such as bread) and is out of sight. What is visible is the part of the mold body that produces spores.
The growth of fungi as hyphae on or in solid substrates is adapted for the efficient extraction of nutrients. Hyphae are specifically adapted for growth on solid surfaces and to invade substrates and tissues. They can exert large penetrative mechanical forces.
Some hyphae grow down into the food material. Cells of the hyphae can produce chemicals that break down the material (fruit, paper, wood) into nutrients that the fungus can absorb.
The structures of fungi vary widely. Some fungi have rigid cellular walls that are made of chitin. Chitin is resistant to breakdown as compared to the cellulose that makes up the cellular walls of plants. Spores can survive a very long time in harsh conditions until the environment is suitable for growth.